Millions of people worldwide suffer from hair loss, which lowers confidence and self-esteem. The causes of hair loss, available treatments, non-surgical and surgical options, and the psychological effects of hair restoration are all covered in this extensive guide.
Introduction to Hair Loss
Alopecia, the medical term for hair loss, is a common condition that affects both men and women. Genetics, hormonal fluctuations, illnesses, drugs, and lifestyle choices can all contribute to it. Determining the best course of action requires an understanding of the underlying cause.
Causes of Hair Loss
- Genetic Factors: The most prevalent cause, androgenetic alopecia, also known as pattern baldness, is inherited from one or both parents.
- Hormonal Changes: Hair thinning or loss may result from hormonal imbalances, such as those that occur during pregnancy, menopause, or thyroid conditions.
- Medical Conditions: Chronic illnesses, autoimmune diseases like alopecia areata, and scalp infections can all cause hair loss.
- Medication: Hair loss is a side effect of some medications used to treat high blood pressure, arthritis, cancer, and depression.
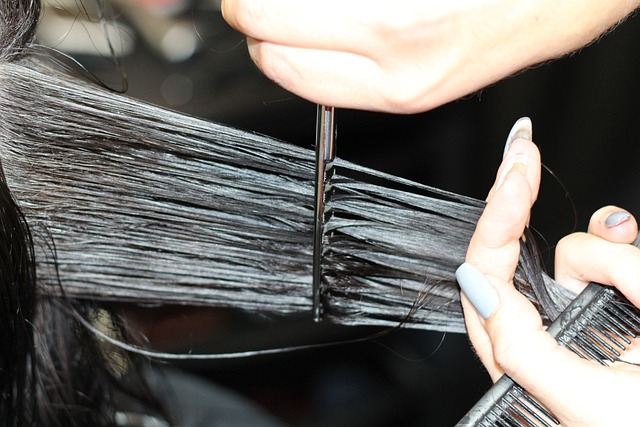

Non-Surgical Hair Restoration Options
- Drugs: By addressing hormonal factors, FDA-approved drugs such as finasteride (Propecia) and minoxidil (Rogaine) encourage hair regrowth and stop additional loss.
- Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): Uses non-invasive laser devices worn at home or in clinics to stimulate hair follicles and encourage hair growth.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: In order to stimulate hair follicles, patients undergoing platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy inject concentrated platelets from their blood into their scalp.
- Topical Treatments: Topical treatments include shampoos, serums, and foams that contain active ingredients that promote hair growth and scalp health, such as peptides or ketoconazole.
Surgical Hair Restoration Techniques
- Hair Transplantation: Hair follicles from donor areas—usually the back of the scalp—are transplanted to balding or thinning areas as the gold standard for permanent hair restoration.
- Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT): involves cutting a strip of scalp from the donor region and dividing it into separate transplantable grafts.
- Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE): involves removing individual follicular units straight from the donor region, leaving as little scarring as possible, without making a linear incision.
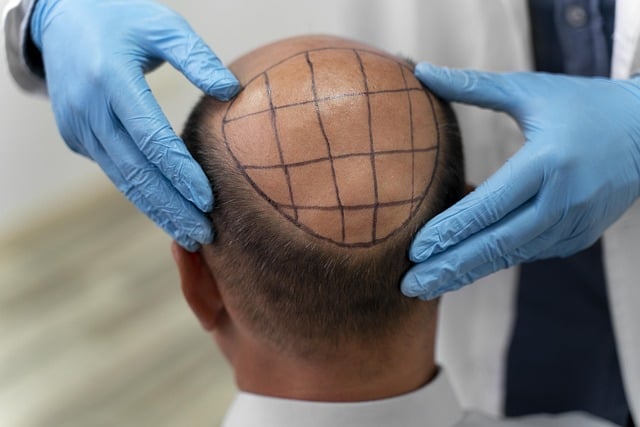
Choosing the Right Hair Restoration Option
- Consultation and Evaluation: To identify the cause of hair loss and suggest appropriate treatments, a skilled dermatologist or hair restoration specialist will conduct a comprehensive evaluation.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: Personalized treatment plans are made according to each patient&8217;s requirements, preferences, medical background, and degree of hair loss.
Psychological Impact of Hair Loss
- Self-Esteem and Body Image: For some people, hair loss can have a detrimental effect on their social interactions, body image, and self-confidence, which can result in anxiety and depression.
- Quality of Life: By boosting general wellbeing and regaining self-esteem, successful hair restoration can greatly improve quality of life.
Lifestyle Tips for Healthy Hair
- Nutrition: Consuming a well-balanced diet full of proteins, vitamins, and minerals that are vital for healthy hair.
- Stress management: lowering stress levels, which can cause hair loss, by engaging in relaxation practices like yoga, meditation, or physical activity.
- Scalp Care: Scalp care includes using mild shampoos that are appropriate for your hair type, avoiding harsh chemicals, and massaging your scalp gently.
Future Trends in Hair Restoration
- Technological Developments: Ongoing studies in gene therapy, nanotechnology, and stem cell therapy for more individualized and efficient hair restoration procedures.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Hair Restoration: AI-powered instruments for accurate hairline design, donor site selection, and treatment outcome prediction.

Conclusion
Options for hair restoration have greatly changed, providing practical ways to stop hair loss and encourage new growth. People can restore their self-esteem and enhance their quality of life by choosing non-surgical therapies or surgical operations like hair transplantation. Determining the best course of treatment requires knowing the causes of hair loss and speaking with an expert.
References
- American Academy of Dermatology. (n.d.). Hair Loss. Retrieved from https://www.aad.org
- International Society of Hair Restoration Surgery. (2023). Hair Loss & Restoration. Retrieved from https://ishrs.org
